OVERVIEW
Zapier remains one of the most accessible and reliable workflow automation tools available. Its combination of simplicity, scale, and stability makes it a go-to choice for individuals and teams that want to automate daily tasks without coding. With 8,000+ app integrations, Zapier offers unmatched reach across business, productivity, and developer tools.
While it may not provide the same deep logic or hosting flexibility as Make or n8n, Zapier’s ease of use and dependable execution set it apart as the most approachable no-code automation platform for general business needs. Its pricing is transparent and predictable, though task caps can limit heavy automation workloads.
BEST FOR:
Pros and cons
Pros
- Extensive integration ecosystem. Zapier connects with over 8,000 apps, making it one of the largest automation libraries available.
- Low-code workflow design. Users can build automations without any coding knowledge. The interface uses simple triggers and actions, making it accessible for anyone who wants to automate repetitive work quickly.
- Transparent pricing model. Every plan clearly shows how tasks are counted and what’s included. This helps teams understand usage, manage costs, and scale automations as they grow.
- Helpful learning resources. Zapier’s Help Center, tutorials, and community forum make it easy to find answers, learn new workflows, and troubleshoot without needing technical support.
Cons
- Hard task caps. Each plan includes a fixed monthly task limit. When data spikes or workflows run more often than expected, Zaps can pause once the cap is reached, potentially interrupting business processes or losing key updates mid-cycle.
- Support tiers vary. Direct, priority support is limited to higher plans, while most users rely on self-serve documentation and the community forum.
- Workflow step and field limits. Zapier caps workflows at 100 steps, including branches, and action steps at 1,000 fields. Large, data-heavy automations may need to be split across multiple Zaps.
- HIPAA limitation. Zapier does not support HIPAA compliance and will not sign Business Associate Agreements (BAAs), preventing use in healthcare or other workflows containing protected health information (PHI).
Key features and ease of use
Zapier makes automation accessible by turning repetitive work into simple, visual workflows called Zaps. Each Zap starts with a trigger and follows with one or more actions, allowing users to link data and processes across thousands of tools. The platform is designed to balance ease of use with enough flexibility for advanced users who want deeper control.
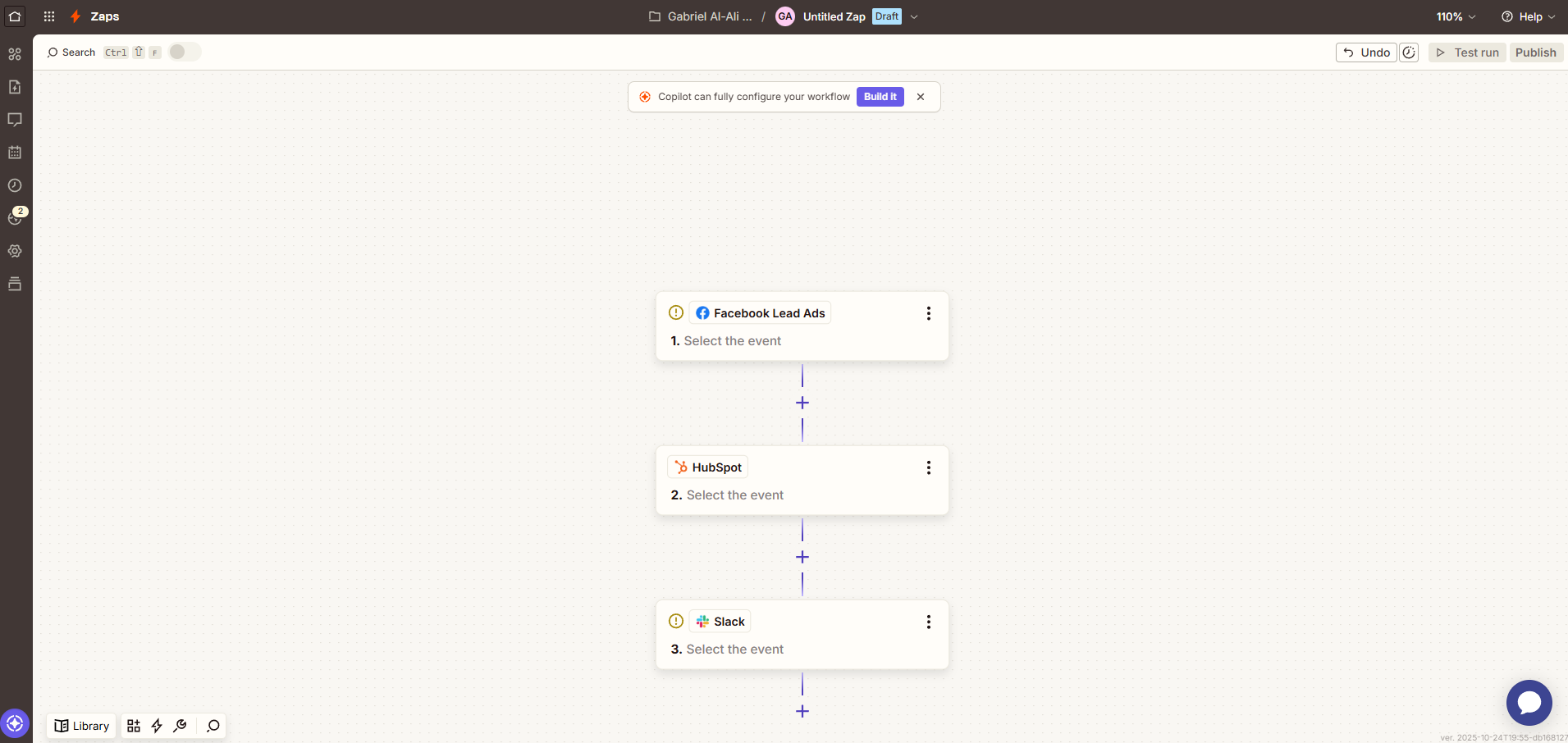
Visual workflow
Zapier’s editor lays out each automation as a clear sequence of steps. Triggers, actions, and conditions are displayed visually, making it easy to see how data moves through a workflow. Setup happens through dropdowns and field mapping, allowing users to define logic without touching code. The interface supports real-time testing so each step can be verified before going live.
Integration library
Zapier connects with 8,000+ apps, making it one of the largest integration ecosystems among automation platforms. It spans every major category, including CRM, marketing, project management, finance, and AI tools. Each integration includes defined triggers and actions that let users send and receive data between apps with minimal setup.
Advanced features
Beyond basic automations, Zapier supports advanced functionality for complex workflows. Users can add filters, delays, and branching paths to control how data flows between steps. Developers can extend functionality through webhooks, API requests, and code blocks that run JavaScript or Python directly within a Zap. The developer platform also allows custom app creation for internal or proprietary systems.
Ease of use
Zapier’s interface is built for simplicity. New users can set up their first automation within minutes, guided by templates and an intuitive editor. As workflows scale, features like folders, naming conventions, and shared access help keep projects organized. While managing large numbers of Zaps can require some structure, the overall experience remains straightforward for most teams.
Zapier suits individuals and businesses that want reliable automation without learning to code. It bridges the gap between simplicity and capability, offering the flexibility to automate nearly any task while staying approachable for everyday users.
Integrations
Zapier’s integration ecosystem is one of its biggest strengths. With support for 8,000+ apps, Zapier offers access to a vast range of tools and systems, making it possible to connect nearly everything a team uses in one place.
Popular integrations includes
- Productivity. Google Workspace, Slack, Microsoft Teams, Notion
- CRM and sales. HubSpot, Salesforce, Pipedrive
- Marketing. Mailchimp, ActiveCampaign, Facebook Ads
- Project management. Asana, Monday.com, ClickUp, Trello
- E-commerce. Shopify, WooCommerce, Stripe
- Developer tools. GitHub, Webflow, Airtable
Depth and reliability
Each app connection includes triggers and actions that define how automations start and what they do. Zapier maintains these integrations regularly to ensure compatibility and adds new tools as platforms evolve. The result is a library that balances scale with dependable performance for day-to-day operations.
Custom flexibility
For tools not already supported, Zapier offers advanced options through its developer platform. Users can create custom integrations or use webhooks and API calls to connect proprietary or niche systems. This ensures nearly any workflow can be automated, even without a prebuilt connector.
Compared to other automation tools, Zapier stands out for its scale and accessibility. Platforms like Make and n8n offer more complex logic and hosting options, but Zapier’s integration reach remains unmatched in the market.
Our featured partners
Zapier pricing tiers
Zapier uses a task-based pricing model, where each completed action within a workflow counts as one task. A task might be sending an email, updating a spreadsheet, or posting a message in Slack. Every plan includes a monthly task limit that resets each billing cycle. Once that limit is reached, Zaps pause until the next cycle or an upgrade is made. This usage-based system keeps pricing predictable but requires careful planning for teams with fluctuating workloads.
| Plan | Annual price (per month) | Monthly price | Includes | Best for |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Free | $0 | $0 | 100 tasks per month, single-step Zaps, access to core apps. | Individuals testing automations. |
| Professional | $129 (10k tasks) | $193.50 (10k tasks) | Multi-step Zaps, unlimited premium apps, webhooks, filters, and formatters. | Freelancers or small teams automating recurring workflows. |
| Team | $169 (10k tasks) | $253.50 (10k tasks) | Shared workspaces, SAML/SSO, folder organization, advanced admin tools. | Growing teams managing multiple users. |
| Enterprise | Custom | Custom | Unlimited users, advanced admin controls, data retention options, dedicated support. | Large organizations with compliance or scale requirements. |
Prices shown reflect plans with 10,000 monthly tasks. Task limits can be increased or lowered depending on workflow volume.
Zapier’s pricing scales with task volume rather than seats or workflow count. This approach gives flexibility to smaller teams while keeping automation costs tied to actual usage. Annual plans offer meaningful savings for consistent workloads, while monthly billing helps teams test and adjust before committing.
Because automations pause when task limits are reached, teams with frequent data surges should plan for buffer capacity. For most users, the model balances accessibility with predictable scaling, allowing automations to grow naturally as workflows expand.
Compliance and security
Security and compliance are central to Zapier’s role as a workflow automation platform that connects business data across multiple tools. The company maintains strict standards for encryption, access control, and infrastructure monitoring to ensure automations remain secure. Its compliance framework aligns with major privacy and data protection regulations, making it suitable for most business and enterprise environments.
Security features
- Data encryption. Zapier encrypts data in transit using TLS 1.2 and secures data at rest with AES-256 encryption.
- Authentication and access control. Two-factor authentication (2FA) and role-based permissions protect user accounts and limit data access.
- Continuous monitoring. A dedicated security team oversees system activity 24/7, supported by penetration testing and a bug bounty program.
- Audit logs and visibility. Enterprise plans include audit trails, IP allowlists, and detailed run logs for governance and change tracking.
- Operational reliability. Zapier’s infrastructure uses automated failover and regular backup processes to maintain uptime and data integrity.
Compliance and certifications
- SOC 2 Type II and SOC 3. Independent audits validate Zapier’s security, availability, and confidentiality controls.
- GDPR and CCPA compliance. The company follows major international privacy frameworks and supports data subject rights requests.
- Data Privacy Framework. Certified under the EU-US Data Privacy Framework for compliant data transfers between regions.
- Data privacy and control. Users retain ownership of their data, and credentials are encrypted with limited internal access.
- HIPAA limitation. Zapier does not sign Business Associate Agreements (BAAs) and is not approved for handling protected health information (PHI).
Zapier provides a strong foundation for security and compliance. However, teams working in healthcare or other regulated industries should note that Zapier is not HIPAA-compliant, and should avoid connecting workflows that include personal health information. For all other use cases, the platform’s safeguards and certifications deliver reliable protection for business automation at scale.
Community and customer support
Zapier offers a layered support model that blends self-serve resources, a robust user community, and direct support teams for paid users. This ensures that both small teams and growing businesses can access help, while high-volume users gain structured assistance for complex workflows.
Support options
- Help Center. A comprehensive knowledge base covering setup, troubleshooting, billing, and workflow design.
- Email support. Available across paid plans, with response times that vary by plan level.
- Live chat. Offered on Professional plans with 2,000 or more monthly tasks, as well as all Team and Enterprise tiers.
- Dedicated technical support. Enterprise customers receive a Technical Account Manager for implementation guidance and troubleshooting.
Community resources
- Zapier Community Forum. A public space where users ask questions, share workflow tips, and collaborate on automation ideas.
- Solution Partner directory. A network of certified experts and agencies that help businesses design or optimize automations.
- Tutorials and training. Self-paced learning materials, product updates, and webinars help users expand their automation skills over time.
Zapier’s support ecosystem works well for users at every stage. Entry-level users benefit from extensive documentation and an active community, while larger teams gain faster response times and dedicated account management through higher-tier plans.
Customer reviews
As of October 2025, Zapier holds strong user satisfaction scores across major review platforms. It rates 4.7/5 on Capterra from over 3,000 verified reviews and 4.5/5 on G2 from more than 1,400 users. Feedback consistently highlights Zapier’s ease of use, wide integration library, and reliability for automating repetitive work.
What people like
- Ease of use. Reviewers frequently mention how simple it is to build automations without coding or technical setup.
- Integration range. Many users praise the wide app coverage, often describing it as the most comprehensive among automation platforms.
- Time savings. Teams report measurable efficiency gains by automating data transfers and routine tasks.
- Workflow reliability. Zaps generally perform consistently once configured, minimizing manual oversight.
- Documentation and templates. Users appreciate the clarity of setup guides and the availability of prebuilt templates to get started faster.
Where people see changes
- Task caps and workflow pauses. When monthly task limits are reached, automations stop running until the next reset or plan upgrade. This can disrupt active workflows and delay important updates.
- Complex workflows require workarounds. While Zapier supports advanced tools like filters, paths, and code steps, some users find that deeply nested or looping automations take extra effort to configure.
- Support responsiveness. Several reviewers report slow replies on lower-tier plans or reliance on the community for answers.
- Learning curve for advanced features. While easy to start with, mastering filters, paths, or code-based actions can take time.
Methodology: How we rate automation platforms
The data-driven approach behind Creative Advisor's platform recommendations.
Star rating categories
Our criteria prioritize the factors that weigh most heavily on platform capability and user satisfaction.
We evaluate the breadth and depth of available connections, assessing whether platforms offer extensive app coverage, advanced features like webhooks and custom APIs, and thorough documentation that enables users to build complex workflows without limitations.
We assess how intuitive the interface is for new users, how quickly teams can onboard, and whether the platform facilitates smooth collaboration across team members. We also assess essential workflow features like conditional branching, advanced scheduling options, and robust error handling with retry capabilities.
We examine whether pricing structures are transparent and competitive, and whether plans scale efficiently as workflow complexity and usage grow.
We verify that platforms meet or exceed industry security standards and maintain transparent, accessible policies around data protection and compliance certifications.
We evaluate the strength of user communities, quality of educational resources, and responsiveness of customer support across multiple channels.
We look for platforms that consistently introduce cutting-edge features, demonstrate a clear product roadmap, and publicly share their commitment to advancing automation technology.
We assess platform uptime, performance speed under various load conditions, and transparency around service status and incident reporting.
We analyze verified user feedback across multiple review platforms, looking for consistent satisfaction patterns and evaluating sentiment.
Creative Advisor rigorously evaluates automation platforms across more than 10 technology providers. Our review process involves gathering over 40 data points, verifying information through company websites and public documentation, and often testing the platforms directly. Our editorial team thoroughly fact-checks all findings and keeps ratings current with regular updates throughout the year.
Article sources
Creative Advisor uses primary sources to verify our claims. We thoroughly fact-check editorial content to ensure the information you're reading is up-to-date and accurate.
- "The secure way to scale AI". Zapier. Reviewed on Oct. 25, 2025.
- "Data Privacy Overview". Zapier. Reviewed on Oct. 25, 2025.
- "Help when you need it, how you need it". Zapier. Reviewed on Oct. 25, 2025.
- "Reviews of Zapier". Capterra. Reviewed on Oct. 25, 2025.
- "Zapier". G2. Reviewed on Oct. 25, 2025.